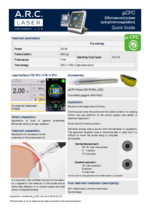
With the µCPC treatment, A.R.C. Laser offers a gentle procedure for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma.
The aim of the treatment is to slightly shrink the ciliary muscle and not to permanently damage the ciliary body. This puts the trabecular meshwork under tension and improves the outflow of aqueous humor.
In contrast to cyclophotocoagulation, with µCPC the laser energy is applied with a slow and continuous sliding movement of the special µCPC probe along the hemispheres. The laser energy is not delivered continuously, but in individual, repetitive laser pulses with a duration of 500 µs each.
Method of treatment
Patient preparation:
Either retro- or peribulbar anesthesia is administered prior to treatment. Alternatively, analog sedation can also be used for µCPC treatment. As with cyclophotocoagulation, the eye to be treated is cleaned, covered and an eyelid retractor is inserted. After rinsing with iodine solution, viscoelastic (e.g. Methocel) is applied to the sclera.
The µCPC treatment
Preparation:
- Select the preset µCPC treatment parameters on the FOX IV 810 by selecting the green µCPC icon
- Set the desired total energy or time on the large, user-friendly touch display
- Check the laser parameters: e.g. power 2.0 Watt, 500 µs pulse duration & 1ms pulse pause (DutyCycle 33.3 %)
- Filling the µCPC probe with viscoelastic (e.g. Methocel)
Treatment:
- Positioning the µCPC probe at the limbus -> fiber tip is 3 mm away from the limbus to irradiate the pars plana localized area of the ciliary body muscle.
- The handpiece is moved along the hemispheres under slight pressure, leaving out the 3 and 9 o'clock positions.
- A total energy of 120 - 140 J is applied to the eye - 60 - 70 J per hemisphere (according to Sanchez et al., the ideal energy window is between 110 and 150 J [1])
- To work at the right speed, an energy input of 10 J per hemisphere with 6 to 7 repetitions is recommended.
- The FOX IV 810 provides support with its smart functions and indicates the energy already applied or remaining energy / time in the form of a voice output at intervals of 10 J or 10 s. In between, the metronome sets the rhythm - an audio signal is emitted every 1 J or 1 s.
- At the end of treatment, the FOX IV 810 displays the individual protocol with all relevant information for documentation purposes.
The above parameters for laser power and total energy refer to the treatment of Caucasian patients.
Our users' experience with African patients shows particularly good results with a total energy of 80 J and a laser power of 1.5 W, as the energy is absorbed more strongly due to the higher pigment content.
Post-operative management after µCPC:
In contrast to cyclophotocoagulation, only the application of anti-inflammatory drugs is induced after µCPC treatment, which are often administered over a shortened duration. In many cases, pain medication can be dispensed with completely.
[1]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6205680/
The µCPC treatment...
Treatment results
Treatment results
The µCPC procedure is characterized by a solid success rate of up to 95 % with a pressure reduction of 30 % to 45 %.
In addition, current data indicates a significant reduction in medication. Visual acuity is maintained, and in some cases even slightly improved.
In conclusion, it can be said that the µCPC procedure can be used much earlier in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma due to its high success rates, good pressure reduction and very few side effects, thus closing the gap between the SLT procedure and conventional cyclophotocoagulation.
CPC and µCPC in comparison
| CPC | µCPC | |
| Type of glaucoma | Open-angle glaucoma | Open-angle glaucoma |
| Effect | Reduction of aqueous humor production | non-damaging - muscle shrinkage |
| Tissue interaction | damaging - coagulation effect | in motion along the hemispheres |
| Application method | punctual | in motion along the hemispheres |
| Patient comfort | painful, often accompanied by intraocular inflammatory reactions | low pain sensation, little to no intraocular inflammatory reactions |
| Side effects | frequent | reduced and temporary |
| Follow-up treatment | pain medication anti-inflammatory drugs | no pain medication shortened treatment duration with anti-inflammatory drugs if necessary |
| IOP reduction | 42 % on average | 38 % on average |
| Standard parameters | 2 W, 2 s per exposure | 2 W, 500 µs at 33 % duty cycle |
CPC
The punctual application of laser energy leads to coagulation of the ciliary body, or more precisely the ciliary villi, and thus achieves a reduction in aqueous humor production.
Due to the high punctual energy density, intraocular inflammation often occurs and other serious side effects such as hypotony and phthisis bulbi can also occur.
CPC treatment procedure
Application of single laser spots evenly distributed over the two hemispheres.
Typical parameters: Power per pulse of 2 W and a pulse duration of 2 s.
An alternative that is increasingly being used is the soft coagulation technique, which applies reduced power over a longer irradiation time.
Typically, treatment is started at 1.2 W and 4 s.
For gentler treatments, the laser power can also be reduced while increasing the application time.
µCPC
In gentle µCPC treatment, the laser energy is delivered to the ciliary muscle in 500 µs pulses and the total energy is applied with low energy density by moving the probe along the hemispheres. By pulsing the laser at a duty cycle of 33.3 %, the thermal effect is greatly reduced compared to cyclophotocoagulation.
As a result, the side effect profile is significantly reduced and the patient's sensation of pain after treatment is almost negligible compared to CPC. Only temporary, superficial irritation of the conjunctiva and sclera occurs, if at all.
µCPC treatment procedure
The lanser energy is transferred into the ciliary body muscle by moving the probe along the hemispheres:
Typical parameters: Power of 2 W applied at a duty cycle of 31.3 % - corresponds to a pulse duration of 500 µs and a pulse pause of 1 ms.
60 - 70 J are applied per hemisphere; the probe is moved 6 to 7 times along the hemisphere for approx. 15 s until 10 J have been applied each time.
The total energy per eye is 120 - 130 J.